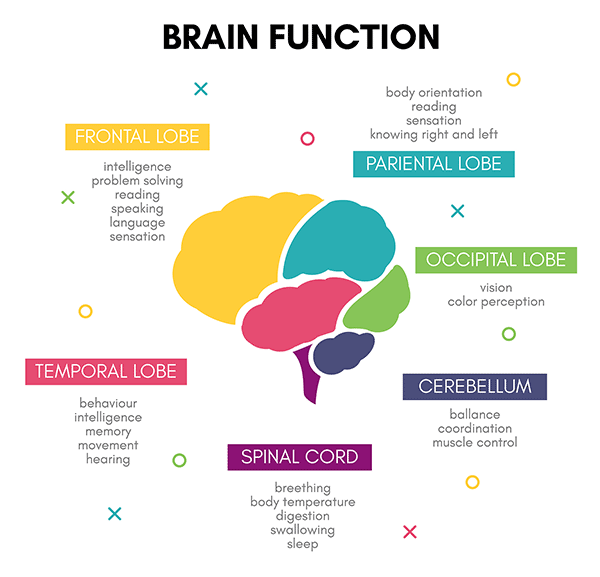
The human brain is the most complex organ in the body, and it is also the site of action for many drugs. To understand how drugs impact the brain, it is first necessary to understand how the brain works.
The brain is made up of billions of neurons, which communicate with each other via electrical signals. These signals are responsible for everything from our thoughts and emotions to our movement and sensory experiences. Drugs can alter these electrical signals in various ways, depending on the drug and its dosage. For example, drugs that increase neurotransmitter activity can cause feelings of euphoria, while drugs that decrease neurotransmitter activity can cause feelings of depression. In some cases, drugs can even change the structure of neurons in areas of the brain, which can lead to long-term changes.
Brain and Addiction
The brain is made up of trillions of cells called neurons. These cells communicate with each other by sending electrical impulses across synapses, which act as bridges between the cells. When a neuron receives an electrical impulse, it sends a chemical message to the next neuron across the synapse. This process allows information to be sent throughout the brain.
Alcohol and drugs can impact this process by affecting how electrical impulses are sent and received, elevating the risk factors.
For over 25 years, people from all over the world have chosen Waismann Method as their opioid detox provider.
We know the challenges you face and the importance of creating a unique and personal experience for you right from the start.
Call for Detox Options 1-800-423-2482
For example, drugs like cocaine and methamphetamine increase the amount of dopamine in the brain, which causes the neurons to fire more frequently. This disruption of the brain circuits can lead to addiction because it creates a sense of pleasure and euphoria. On the other hand, drugs like alcohol and sedatives depress the central nervous system, which slows down the communication between neurons. Other drugs have different impacts on the brain. For example, some drugs, like marijuana, can interfere with the communication between neurons and lead to thinking, learning, and memory problems. Drugs like cocaine or methamphetamine can cause nerve cells to die, leading to permanent changes in the brain’s structure and function.
Drug addiction is a complex disease that affects the brain in multiple ways. When someone uses drugs, it can change the way their brain functions. These changes can be short-term or long-term, leading to damaging consequences.
Drugs and the Brain
One of the most significant impacts of drug use on the brain is addiction.
Addiction is a physiological condition characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use despite negative consequences.
When someone is addicted to drugs, they will continue to use them even if it causes problems in their life. For example, someone addicted to drugs may continue to use them even if it means losing their job or destroying their relationships.
Addiction alters your mental health in so many ways because it disrupts how the brain works and alters its structure, allowing us to process information. These changes can be long-lasting and lead to memory, learning, and decision-making problems.
Drugs can profoundly impact the brain, often altering vital areas for life-sustaining functions. One of the most critical brain areas affected by drugs is the cortex, which is responsible for controlling movement, thought processes, and emotions.
Drug use can also impact areas of the brain that are responsible for regulating essential bodily functions such as heart rate and breathing.
Drug addiction can lead to long-term changes in the brain’s functions, which can be difficult to reverse even after a person stops using drugs. Some people who abuse drugs may experience problems with thinking or memory, and they may also be more likely to suffer from mental health conditions such as depression or anxiety.
Some of the other impacts of drug use on the brain include:
- Impaired judgment and decision-making
- Changes in mood and behavior
- Problems with memory
There are a variety of treatments available for people who are struggling with drug addiction. Some of these treatments include behavioral therapies, medication, and medically assisted detoxification. Behavioral therapies help patients change their behavior and thought patterns. Medically assisted detox provides the medical support and management to overcome drug withdrawals to achieve complete detoxification successfully. Drug users can use specific medications to manage anxiety, depression, and cravings.
Any drug use, whether prescription medication or illegal drugs, can seriously impact one’s health. Some drugs can be completely reversed with treatment, while others may cause permanent damage that cannot be undone.
It’s essential to seek professional help immediately if you are struggling with addiction in order to get the best possible chance for a complete and successful recovery.
How Science Is Changing the Way We Understand and Treat Drug Addiction
Throughout history, people had powerful misconceptions about the nature of addiction and those who suffered from it. Those suffering from substance use disorders were seen as morally flawed and lacking willpower. Unfortunately, the lack of understanding shaped society’s view and treated addiction.
Today, science has given us a much better understanding of addiction and its causes. We now know that addiction is a physiological disease that affects the brain and can be effectively treated. The stigma surrounding addiction has begun to fade as we have gained a greater understanding of the disease.
Scientists have found that addiction changes the way the brain works, and it affects the areas of the brain that are responsible for judgment, decision-making, and self-control. These changes make it very difficult for someone struggling with addiction to stop using drugs, even when they want to.
Fortunately, there are now effective treatments available for addiction. With the help of these treatments, people with addiction can recover and lead healthy, productive lives. Today, science continues to illuminate the subject by providing us with new discoveries and better understanding. This new understanding has led to a shift in how society responds to drug use, with an emphasis on prevention and treatment instead of punishment.
Conclusion
Addiction is a medical disorder that affects the brain and changes behavior. The understanding of addiction has come a long way in recent years, and we are now able to develop effective prevention and treatment approaches because of this knowledge. As a result of scientific research, we are beginning to understand the genetic variations that contribute to the development and progression of this disorder. Scientists use this knowledge to develop effective prevention and treatment approaches that reduce the toll drug use takes on individuals, families, and communities. We must continue the research in order to find new ways to help those affected by addiction.
Sources:
- NIH: The Science of Drug Use and Addiction: The Basics
- Addiction Science
- NIH: How Science Has Revolutionized the Understanding of Drug Addiction
- NIH: Introducing the Human Brain
- NIH News in Health: Biology of Addiction Drugs and Alcohol Can Hijack Your Brain
Reviewed by Clare Waismann, Registered Addiction Specialist (RAS), Substance Use Disorder Certified Counselor (SUDCC), founder of Waismann Method® Advanced Treatment for Opiate Dependence and Domus Retreat®. Clare Waismann is an authority and expert on opioid dependence, opioid use disorder, substance dependence, detoxification treatments, detox recovery, and other topics covered on RapidDetox.com.